INP-WealthPk
Arooj Zulfiqar
Pakistan’s economy has shown encouraging developments in the first two months of FY25, with improvements in several key indicators as inflation has dropped to single digits, industrial output is on the rise, and large exporting sectors have witnessed growth, painting a positive outlook for the country’s exports, reports WealthPK.
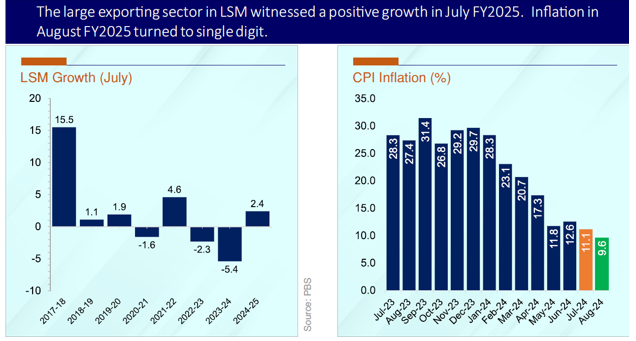
According to the data released by the Ministry of Finance in its monthly outlook for September, the Large-Scale Manufacturing (LSM) sector, which had been contracting, rebounded with a 2.4% growth in July 2024 compared to a 5.4% contraction in July 2023. Out of the 22 monitored sectors, 14 recorded positive growth, with notable performances from key industries, including textiles, food, beverages, wearing apparel, chemicals, automobiles, and paper and board. The textile sector, with the largest weight in LSM (18.2%), returned to positive growth after two years of stagnation. Additionally, the automotive industry also saw substantial growth, with overall vehicle production increasing by 19.5% and sales by 16.3% during the July-August period of FY25. Notably, the production of cars rose by 15%, while trucks and buses surged by an impressive 120.4%. However, tractor production declined 26.9% during the same period. However, while several sectors showed growth, the cement industry faced challenges. Total cement dispatches during 2MFY25 were 6.4 million tonnes, a 17.8% drop from the same period last year.
Domestic dispatches were down by 20.7%, while exports experienced a marginal 1.6% decline. Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation saw a sharp drop, falling to 9.6% in August 2024, the lowest in 34 months. This was a significant decrease compared to the 27.4% inflation rate recorded in August 2023. Month-on-month, inflation rose by only 0.4%, reflecting the easing of inflationary pressures. In July 2024, Pakistan's fiscal sector remained strong, with net federal revenues growing by 7.2% year-on-year to Rs408.4 billion. This growth was largely driven by a 22.6% increase in tax collection and a 20.5% rise in non-tax revenue, primarily from the petroleum levy, which amounted to Rs83.6 billion. On the expenditure side, total expenditures grew by 19.2%, leading to a fiscal deficit of 0.3% of GDP. Despite the fiscal deficit, the primary balance remained in surplus at 0.1% of GDP. FBR's net tax collection for 2MFY25 grew by 20.6%, reaching Rs1,456 billion compared to Rs1,207.5 billion during the same period of FY24. In August 2024 alone, tax collection surged by 19%. Pakistan’s external account also showed improvement, with the current account deficit shrinking to $0.2 billion during 2MFY25 from $0.9 billion in the same period last year.
In August 2024, the current account recorded a $75 million surplus. Goods exports rose by 7.2% to $4.9 billion, while imports increased to $9.5 billion, leading to a trade deficit of $4.7 billion. Key export items such as rice (98.6%), fruits & vegetables (26.7%), and readymade garments (17.9%) posted strong growth. In response to reduced inflationary pressures and improved business confidence, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) cut the policy rate by 200 basis points, bringing it down to 17.5% in September 2024. Meanwhile, the Pakistan Stock Exchange continued its upward trend, with the KSE-100 index closing at 78,488 points in August 2024, gaining 601 points during the month. Market capitalisation increased by Rs117 billion, settling at Rs10,485 billion. With inflation under control, industrial output rising, and exports strengthening, Pakistan’s economy appears to be on a path of recovery. As key sectors continue to expand, this positive trajectory will continue in the coming months, bolstered by prudent fiscal management, policy support and a growing external account.
Credit: INP-WealthPk