INP-WealthPk
Ahmed Khan Malik
The Sindh government has formulated a comprehensive sustainable forest management policy to enhance forest cover, support local livelihoods, and mitigate environmental challenges, reports WealthPK.

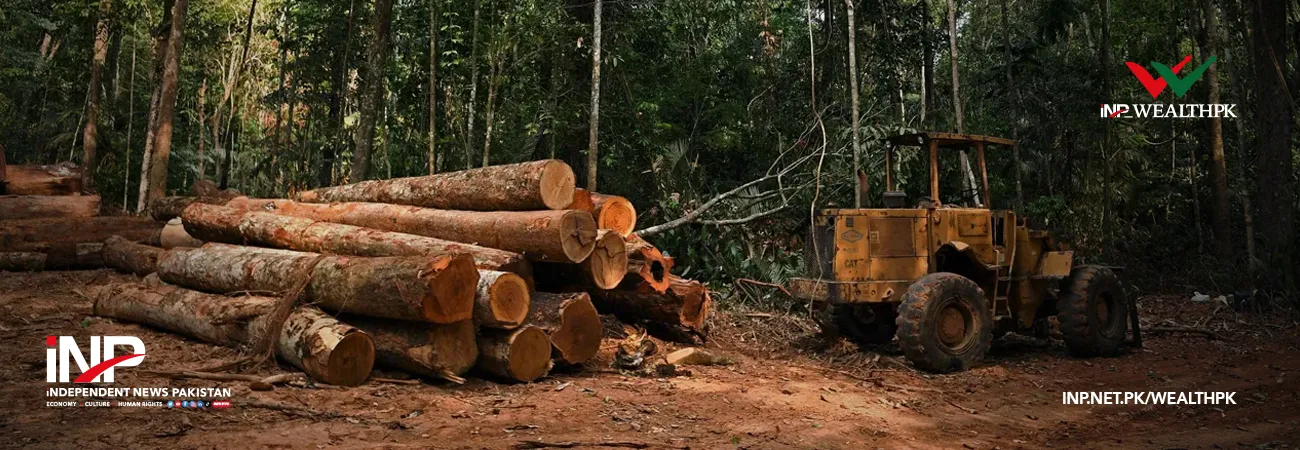
Systematic deforestation over the last many decades has deprived the province of its massive forest cover, bringing it down to less than 2 percent. The existing forests are classified as riverine, irrigated plantations and mangrove forests.
According to official statistics, the riverine forests have declined to 0.05 million hectares (0.35pc), irrigated forests to 0.082 million hectares (0.14pc), and mangrove forests to 0.2 million hectares (1.41pc). The overall forest cover has fallen to 1.9pc.
“The sustainable forest management policy emphasizes community participation in afforestation efforts, particularly in riverine and irrigated plantations, to restore the degraded forests and promote sustainable management practices,” Ubaid Soomro, Director of Forest Department, told WealthPK.

The key strategies outlined in the policy aim to involve the local communities in afforestation and forest protection initiatives to ensure sustainable management, provide economic benefits, and develop and implement plans that balance ecological conservation with economic utilization of forest resources.
Also, expanding forest cover through targeted planting initiatives, particularly in degraded areas, has been targeted in the policy. The policy will also cover the implementation of projects that enhance the capacity of forests to absorb carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
It aims to leverage forestation for economic uplift by creating employment opportunities in planting, maintaining, and managing forests. Sustainable harvesting of non-timber forest products can provide additional income streams for the local communities.
Environmentally, he said, increased forest cover contributes to carbon sequestration, reduces greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere, and plays a crucial role in preventing soil erosion, regulating water cycles, and preserving biodiversity, all of which are vital for climate change adaptation and mitigation.
Soomro said the Sindh Forest Department has initiated several projects under the REDD+ framework (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) to promote sustainable forest management. These projects focus on activities such as forest inventory, carbon stock assessment, community engagement, and development of monitoring systems.
Collaborations with international organizations, including the World Bank and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), have been established to support these initiatives. Despite these efforts, challenges such as land encroachments, illegal logging, and impacts of climate change persist.
Addressing these issues requires continuous policy evaluation, strengthening law enforcement, and enhancing community awareness and participation, he said. The policy underscores the need for substantial investment and technical support to achieve its objectives. He noted that the forest management policy represents a strategic approach to utilizing forestation as a means for economic development and climate resilience.
Through community involvement, sustainable practices, and international cooperation, the province aims to restore its forest ecosystems for the benefit of both its people and the environment, added the Forest Department director.
Credit: INP-WealthPk