INP-WealthPk
Arooj Zulfiqar
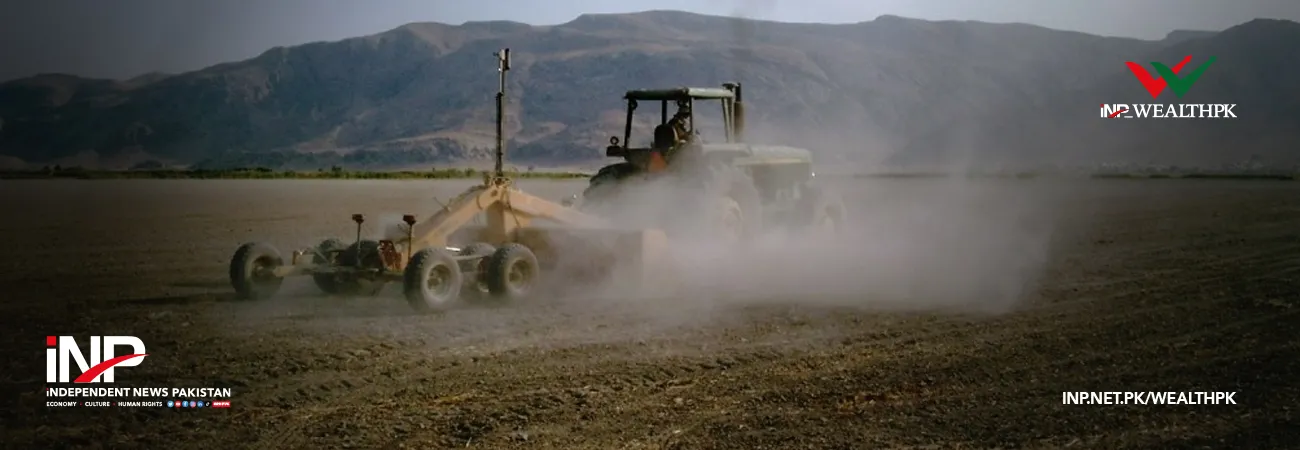
The growing challenge of water scarcity underscores the need for innovative approaches to optimize the available water resources and maintain agricultural yields, reports WealthPK. A key strategy to mitigate water scarcity is enhancing water productivity at the agricultural level. Precision Land Leveling (PLL) is a mechanical process that precisely grades and smoothens land surfaces to achieve consistent plains with minimal fluctuation. Traditionally, PLL involves earth movement using bucket-type soil scrapers and tractor-mounted back blades. However, an effective method to increase water productivity is employing the LASER (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) technology in land leveling. According to Tariq Sultan, Principal Scientific Officer at the National Agricultural Research Centre, the dwindling groundwater supply for irrigation poses a significant threat to agriculture. He highlighted the importance of regulations in incentivizing farmers to adopt water-saving technologies, emphasizing that water scarcity is a major factor limiting crop production.
Tariq noted that the scarcity level of water is not adequately reflected in water prices, leading many farmers in Pakistan to rely on private tube wells due to unpredictable canal water deliveries, thereby straining the groundwater supplies. The precision land leveling project in Pakistan, using the LASER technology, has proved highly beneficial in reducing the operating costs, ensuring accuracy, saving irrigation water, promoting uniform seed germination, improving fertilizer efficiency, and increasing agricultural yields. The senior scientist recalled an impact assessment conducted in 2018, showing 25% increase in water conservation, 23% rise in crop yield, 11% improvement in fertilizer efficiency, and 18% reduction in on-farm labor savings. Despite numerous advantages, the LASER land leveling technology is not widely adopted in emerging and impoverished countries, requiring comprehensive research, extension, participatory, economic, and policy measures to promote its widespread use and ensure long-term sustainability. Highlighting water shortage in Pakistan, Tariq said that while 65 million acre-feet of water is needed for irrigation, only 45 million acre-feet is available through canals, lakes, and tube wells.
This shortfall negatively impacts agricultural production, leading to increased per-acre production costs. Uneven water distribution, with higher areas receiving insufficient water and lower lands experiencing water accumulation, causes root rot, thus further exacerbating the issue. Tariq emphasized the importance of embracing innovative technologies like LASER soil levelers to enhance per-acre productivity. The LASER land leveling approach has demonstrated its efficacy in optimizing resource use, enhancing efficiency, and ultimately contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. However, widespread adoption of this technology faces hurdles in emerging and economically disadvantaged nations, demanding a concerted effort in research, extension services, participatory engagement, and supportive policies. As water remains a pivotal factor in agricultural production, adoption of precision land leveling technologies emerges as a key pathway to address water scarcity, promote water conservation, and secure long-term viability of agricultural systems in the face of evolving environmental challenges.
Credit: INP-WealthPk