INP-WealthPk
Ayesha Mudassar
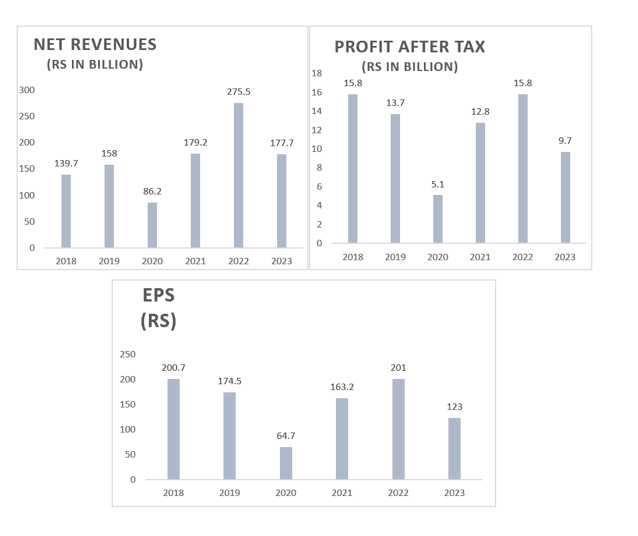
Indus Motor Company Limited's (INDU) net revenue, profit-before-tax (PBT) and profit-after-tax (PAT) fell by 35%, 34% and 39%, respectively, in the last fiscal year (FY23) compared to FY22, reports WealthPK. The decline in net sales turnover and profitability was mainly due to lower sales volume of Completely Knocked-Down (CKD) and Completely Built Unit (CBU) vehicles, on account of import restrictions and demand contraction. The company earned a net revenue of Rs177.7 billion and PBT of Rs16.8 billion. INDU posted a PAT of Rs9.7 billion and earnings per share (EPS) of Rs123 in FY23.
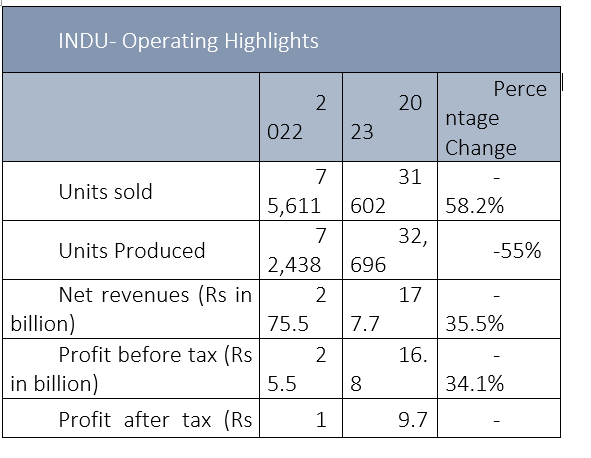
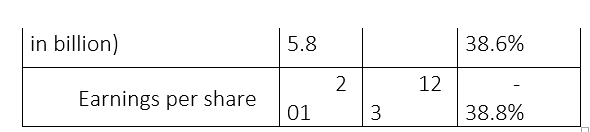
In comparison to FY22, the revenue of the leading automobile assembler in Pakistan dropped by 35.5% from Rs275.5 billion to Rs177.7 billion in FY23. Likewise, the PBT of Rs25.5 billion in FY22 plunged 34% in FY23. INDU's PAT of Rs15.8 billion declared in FY22 also crashed to Rs9.7 billion. During the year ended June 30, 2023, the sales volume of CKD and CBU vehicles decreased by 58.2% to 31,602 units as against 75,611 units sold last year. The depressed demand is primarily due to higher prices and record-high interest rates.
The company produced 32,696 units for FY23, a significant decrease from the 72,438 units produced in FY22. Furthermore, INDU contributed a sum of Rs84.8 billion to the national exchequer as compared to Rs101.4 billion in FY22. Throughout FY23, the automotive industry had to face import compression measures, which were introduced to address the balance of payment crisis and to promote local production. However, these restrictions on essential components created immense challenges for the manufacturing processes, which also led to disruption in the vendor supply chain, frequent plant shutdowns, and underutilisation of the company's plant capacity.
Devaluation, rising inflation, and stringent fiscal measures have driven car prices out of reach for millions. Potential buyers are experiencing unprecedented late delivery times and non-availability of desired car variants due to disruption in supplies. Moreover, the increased tax burden further constrained the sector’s growth potential. The unstable political conditions further eroded consumer confidence, adding to the industry’s challenges.
INDU- historical analysis
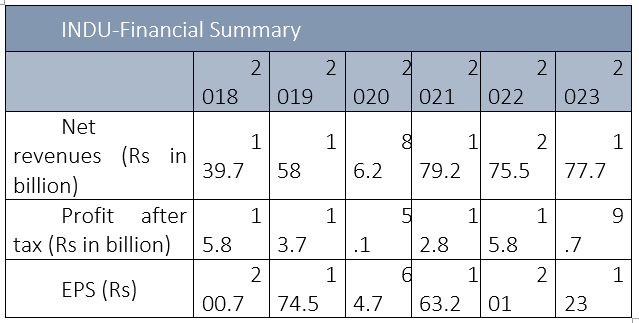
The company's financial performance was exceptional in previous years. However, due to a decline in sales of vehicles, FY23 saw a major decline in profitability. The continuous depreciation of the rupee against the US dollar and the rise in inflation are vital factors that have affected the industry’s volume.
Principal activities of the company
Indus Motor Company was incorporated in Pakistan as a public limited company in December 1989 and started commercial production in May 1993. Registered on Pakistan Stock Exchange (PSX) with the symbol 'INDU', the company is the largest entity in the automobile assembler sector with a market capitalisation of Rs70.1 billion. The primary activities of the company include assembling, progressive manufacturing, and marketing Toyota vehicles in Pakistan. With over 50 partner manufacturers contributing to the value chain by producing parts worth over Rs250 million each working day, the company has played a critical role in developing the local automotive ecosystem. A total of 53 independently owned authorised dealerships that offer after-sales service to consumers have also been established by the company, creating job opportunities for approximately 450,000 people in Pakistan, both directly and indirectly.
Credit: INP-WealthPk