INP-WealthPk
Ayesha Mudassar
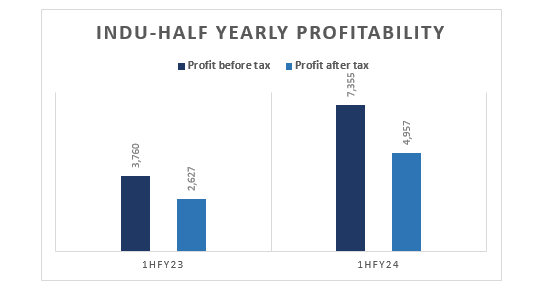
The gross profit of Indus Motor Company Limited (INDU) increased by a significant 266%, profit-before-tax (PBT) by 96% and profit-after-tax (PAT) by 89%, respectively, in the first half of the current fiscal year (1HFY24) as compared to the corresponding period of FY23, reports WealthPK. The automaker earned a gross profit of Rs4.7 billion, PBT of Rs7.3 billion, PAT of Rs4.9 billion and earnings per share (EPS) of Rs63.07 in 1HFY24.
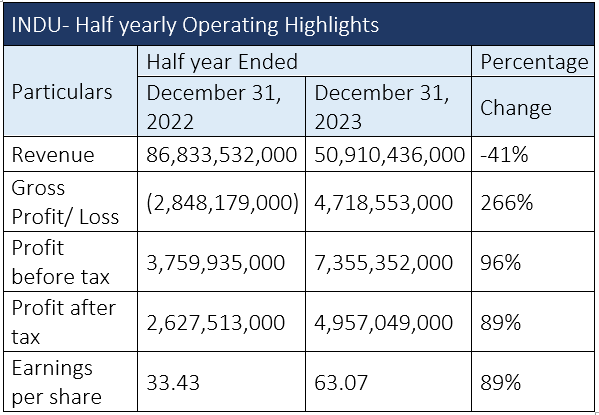
However, during 1HFY24, the auto assembler posted revenue of Rs50.9 billion compared to Rs86.8 billion in the same period of
the previous year, posting a decline of 41%.
Performance over last four years (2020-23)
The company's financial performance remained exceptional over the past years, except in 2023 when sales of vehicles declined, leading to a major cut in the firm's profitability. The net sales turnover increased by 108% to Rs179.1 billion in FY21 compared to Rs86.1 billion in FY20, while net profit for the year also increased to Rs12.8 billion from Rs5 billion in FY20. The increase in turnover and profitability was mainly due to improved economic conditions and healthy demand generated on account of the launch of the facelift models of Corolla, Hilux and Fortuner, along with broader acceptance of Toyota Yaris. In FY22, the company's net sales increased by 54% to clock in at Rs275.5 billion. Likewise, the net profit also experienced a 23% rise on account of higher sales volume of completely and semi-knocked-down kits.
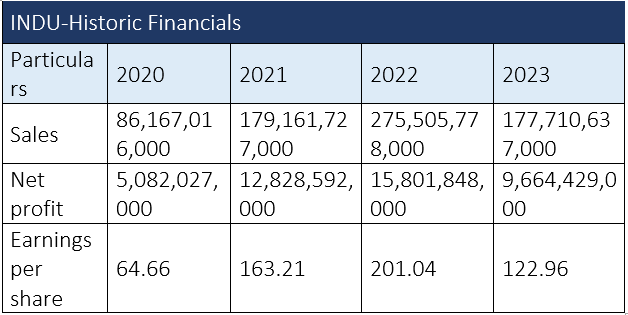
The FY23 witnessed a contraction of 35% and 39% in sales and net profit. This was mainly due to import restrictions, massive currency depreciation and high inflationary pressures.
Profitability ratios (2020-23)
The gross profit margin, a crucial indicator of how efficiently a company manages its production costs, has declined over the years, reaching 4.46% in FY23, down from 8.65% in FY20, 9.30% in FY21 and 6.68% in FY22. This steady downward trend reflects the company's inability to implement effective cost management and pricing strategies, contributing to a lower bottom line.
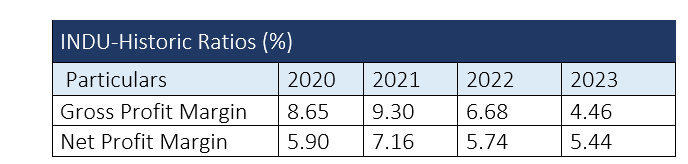
The net profit margin for Indus Motor Company also experienced negative growth, declining to 5.44% in FY23 compared to 5.90% in FY20, 7.16% in FY21 and 5.74% in FY22.
Company profile
Indus Motor Company was incorporated in Pakistan as a public limited company in December 1989 and started commercial production in May 1993. Registered on the Pakistan Stock Exchange with the symbol "INDU", the company is the largest entity in the automobile assembler sector with a market capitalisation of Rs70.1 billion. The primary activities of the company include assembling, progressive manufacturing and marketing Toyota vehicles in Pakistan.
Future outlook
Auto sector volumes are expected to remain relatively low in the upcoming quarters as compared to the previous year's volumes. The import of used cars has been normalised due to the relaxation of the import and taxation regime, whereas locally-manufactured vehicles are subject to consistent rises in duties and taxes, which is a cause for concern.
Pakistan's automobile industry
Throughout 1HFY24, the automotive industry continued to face challenges in terms of higher interest rates, greater duties and taxes, low auto finance availability, and reduced purchasing power of consumers. Consequential to the stated factors, the auto sector operated below 30% production capacity, which led to frequent plant shutdowns. During the six months, the total sales of members of the Pakistan Automotive Manufacturers Association for locally manufactured passenger cars and light commercial vehicles decreased by 54% to 39,104 units, against 84,116 units sold in the corresponding period of last year.
Credit: INP-WealthPk