INP-WealthPk
Azeem Ahmed Khan
Hydroponic farming offers a viable solution to Pakistan's agricultural challenges, including water scarcity, soil degradation, climate change, and sustainable food production, says Agri Advisor Concave AGRI, Muhammad Rizwan.
Talking to WealthPK, Rizwan explained that hydroponic farming serves as an alternative to traditional soil-based agriculture. This method involves growing plants without soil, using a nutrient-rich water solution in controlled environments such as greenhouses or indoor spaces, where the roots are submerged or suspended in water, he added. He highlighted that hydroponics could be effectively used to grow a variety of crops, including vegetables, salads, herbs, fruits, cut flowers, and grasses in Pakistan.
The system uses growing media like rock wool, coconut fiber, peat, perlite, and vermiculite to support plants mechanically, he added. Rizwan noted that traditional farming faced challenges such as requiring large spaces, significant labor, and high water usage, with soil availability being an issue in the urban areas. Hydroponics, however, offers higher productivity and quality, as the plants grow faster and yield more due to receiving all necessary nutrients in an optimized environment.
This system also allows year-round organic crop production, ensuring a consistent supply of fresh produce even in off-seasons, he added. In water-scarce Pakistan, he said, hydroponics was especially beneficial as it used up to 90% less water than conventional farming. The closed-loop irrigation system recirculates water, minimizing waste and reducing overall consumption, he added. Rizwan said hydroponic systems could be set up in urban spaces, greenhouses, or even indoors, making it possible to grow crops in controlled environments unaffected by climate issues like inconsistent rainfall.
Additionally, a controlled setting reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, leading to healthier crops and a cleaner environment, he added. This method also addresses soil erosion and degradation, a major issue in Pakistan, by eliminating the need for soil. Hydroponic farming can be practiced in urban areas, enabling local food production, reducing transportation costs, and minimizing the carbon footprint, he said. Despite numerous benefits, there are challenges to the adoption of hydroponics in Pakistan.
The initial setup cost can be high, especially for the small-scale farmers, as the infrastructure - such as pumps, pipes, reservoirs, and specialized equipment - can be expensive. Many farmers are also unfamiliar with this technology, necessitating extensive training and awareness programs to help them understand its benefits and techniques, he added. Rizwan said hydroponic systems required regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure optimal water quality, nutrient levels, and pH for plant growth.
The farmers need access to technical expertise to resolve any issues that may arise, which can require specialized knowledge, he added. Additionally, many hydroponic systems, particularly those in greenhouses or indoor settings, rely on electricity for pumps, lights, and climate control, he said. In areas with unreliable power supply, this dependency may pose a challenge, requiring backup solutions like generators or solar power, he added. However, despite these obstacles, hydroponic farming holds a significant promise for Pakistan.
The government and private sector have started recognizing its potential, and efforts to promote hydroponics through pilot projects, training programs, and financial incentives are growing, he added. Recently, there has been a rise in hydroponic farms and businesses, particularly in urban areas, he observed. Universities and agricultural research institutions are also focusing on hydroponic research and development, which will help improve the technology and make it more accessible in future, he added.
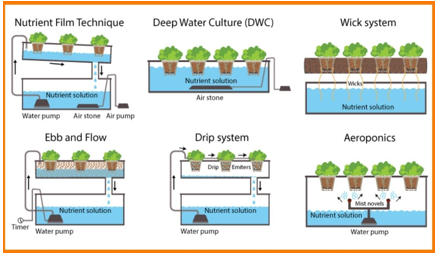
Rizwan also described five common types of hydroponic systems: Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Aeroponics, Deep Water Culture (DWC), Vertical Hydroponic Systems, and Wick System.In NFT, a thin film of nutrient-rich water flows over the roots, constantly recirculating. In aeroponics, the roots are suspended in the air and misted with nutrient solutions to provide efficient oxygen.
DWC involves submerging plant roots in nutrient-rich water, ensuring constant nutrition. Vertical Hydroponic System stacks plants vertically to maximize space, while Wick System uses a wick to draw nutrients to the roots, making it ideal for small-scale setups, he said.
Credit: INP-WealthPk




