INP-WealthPk
Faiza Tehseen
Pakistan is endowed with abundant chlorite deposits awaiting exploitation and processing not only to meet the needs of the domestic industry but also to save the hard-earned foreign exchange spent on the import of chlorite-based products.

Talking to WealthPK about chlorite in its mineral form in Pakistan, Principal Geologist at the Islamabad-based Global Mining Company Muhammad Yaqub Shah said chlorites were widespread phyllosilicate or layer silicate minerals occurring in both clay-grade and macroscopic sizes. These types of minerals commonly happen in sedimentary, hydrothermally altered igneous and low-grade metamorphic rocks. Typically, greenschists or chlorite schists are formed by the metamorphism of basalt or other low silica volcanic rocks. In Pakistan, both the sedimentary and igneous rocks are found in abundance. The common rock types in the Himalayan region are metamorphic like schists, slates, gneisses, phyllites, marbles, and some quartz.
Some outcrops of quartzites and phyllites occur in the northern parts of the Indus basin (this area lies between Sargodha and Shah Kot). The common types of igneous rocks like dolerite, gabbro, diorite, granite, and syenite mostly occur in the areas of Swat, Chitral, Dir, Chagai, Zhob, Nagarparkar and Lasbella. Sedimentary rocks abundantly occur across Pakistan. Indus Basin (both lower and upper), and Balochistan Basins are also considered the two main sedimentary basins. Pyroxene, amphibole, mica, olivine, and garnet are source minerals of chlorite, commonly occurring in sedimentary rocks.

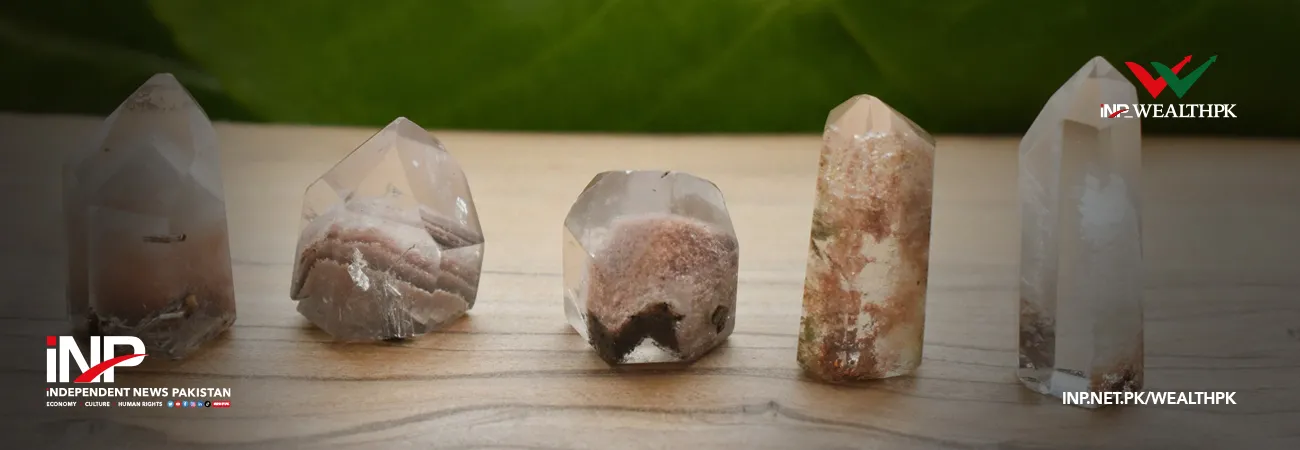
The color of chlorite ranges from colorless to pale or medium green shades. It is rarely found in dark green or other colours but is considered as a prized gem. Chlorite-included quartz crystals are also valued as gems. Such types of quartz crystals are known as ‘chlorite phantom quartz’. The chlorite inclusions in quartz have intriguing shades of green, making it more valuable, added Muhammad Yaqub. “There are several uses of chlorite in both mineral and chemical forms. Most of the chlorite minerals have a foliated appearance and a soapy feeling to the touch. “It is also intermixed with other minerals. Sometimes, it occurs as a finely-grained magnesium chlorite, resembling talc.
This quality makes it ideal for use in the ceramic industry and paint applications. “Chlorite can be used as a catalytic agent and replacement for pyrophyllite as an industrial filler in the rubber and plastic industry. Chlorite solutions are used in the oil and gas industry to stabilize the drilling and viscosity control of mud applications,” he elaborated. Chlorite of sodium is largely used as a bleaching agent in the pulp and paper industry. It is more environment-friendly than chlorine. Compounds of chlorite are used in laboratories for biomedical research. Derivatives of chlorite compounds like chlorine are useful in a variety of industrial productions and processes.
In the agriculture sector, it is used to sanitize equipment, disinfect the irrigation water, and control bacterial and fungal diseases. Chlorine dioxide is useful as a food disinfectant, a mildew and mold remediator in buildings; a disinfectant and sanitizer in hospitals; and a treatment agent of municipal and industrial water. Keeping in view the value of diverse chlorites, Pakistan needs to emphasize its indigenous extraction from different mediums. In lumpy, powdered, paste, or any other industrially required form, it can not only be used locally but can be exported as well. It is a fact that the wide need for chlorite for multiple industrial uses may cause new work opportunities and revenue generation sources. Decision-makers in Pakistan must focus on its processing.
Credit: INP-WealthPk